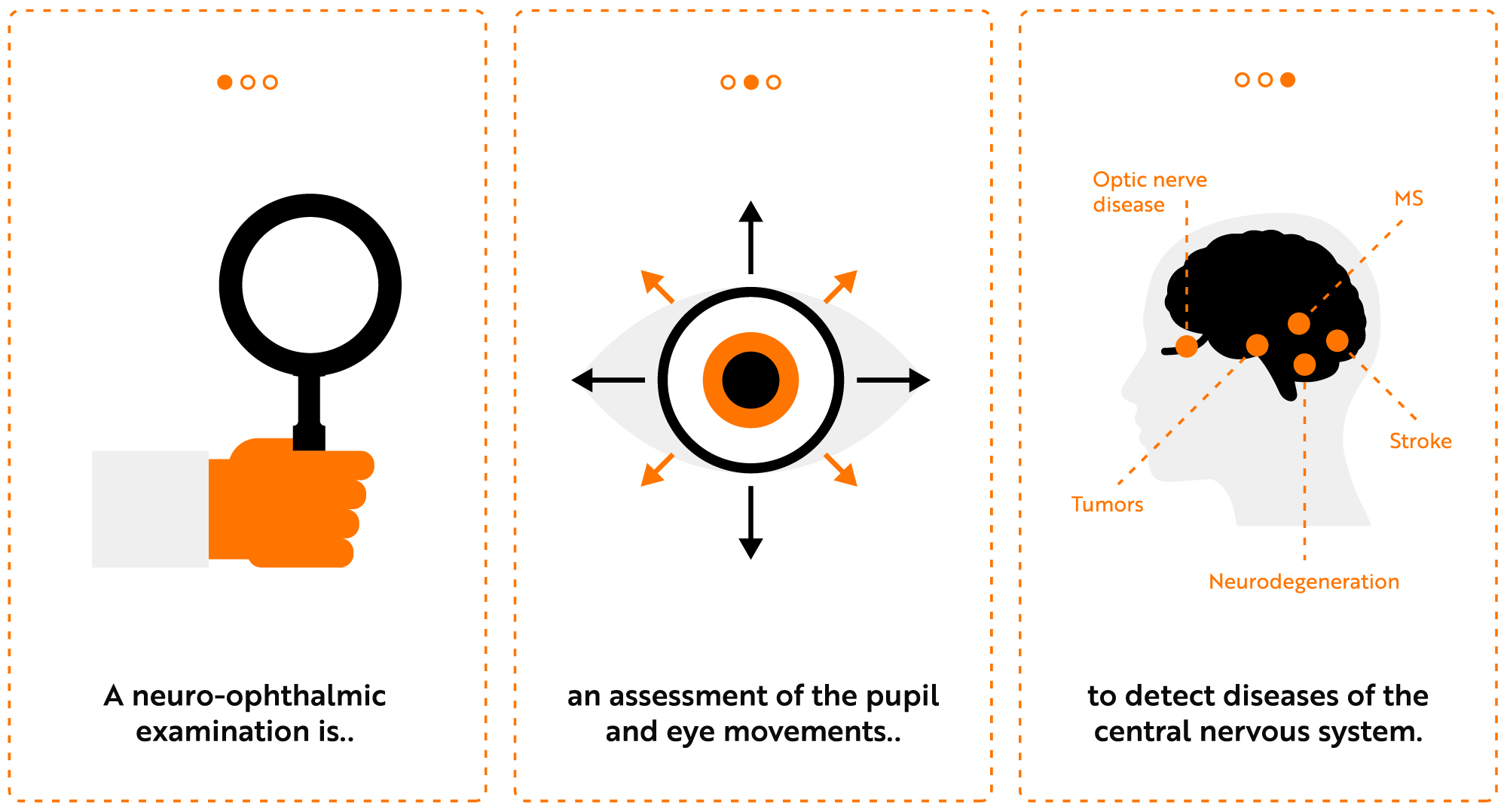
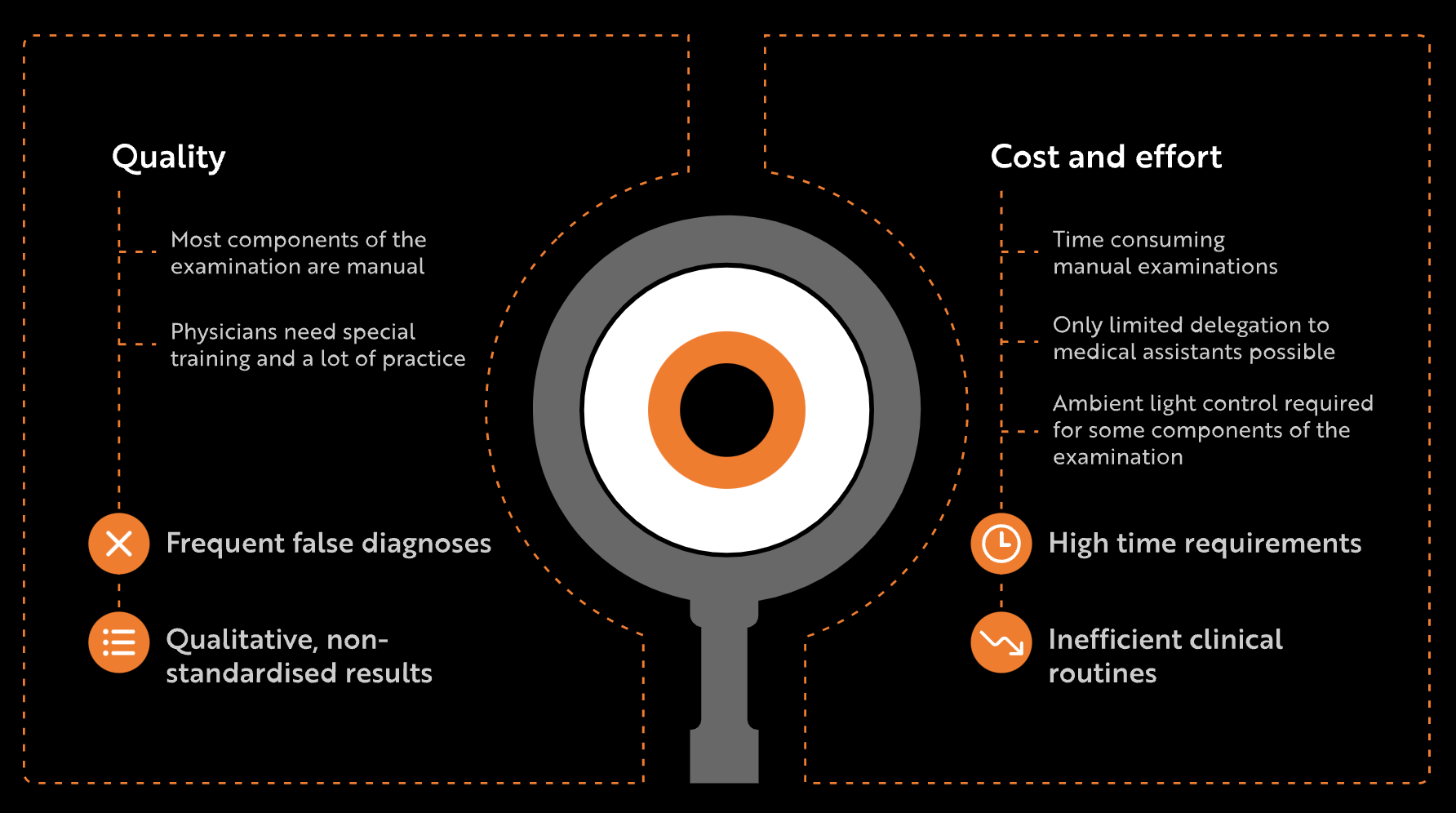
Virtual Reality Pupillography swings the flashlight on Glaucoma Management
RAPD measurements reliably detected asymmetries in optic nerve damage in glaucoma patients. SAP and RAPD combined led to an improved prediction of RNFL thickness, as measured by OCT.