It was our pleasure to meet you!
Our conference highlight
POSTER ID P784
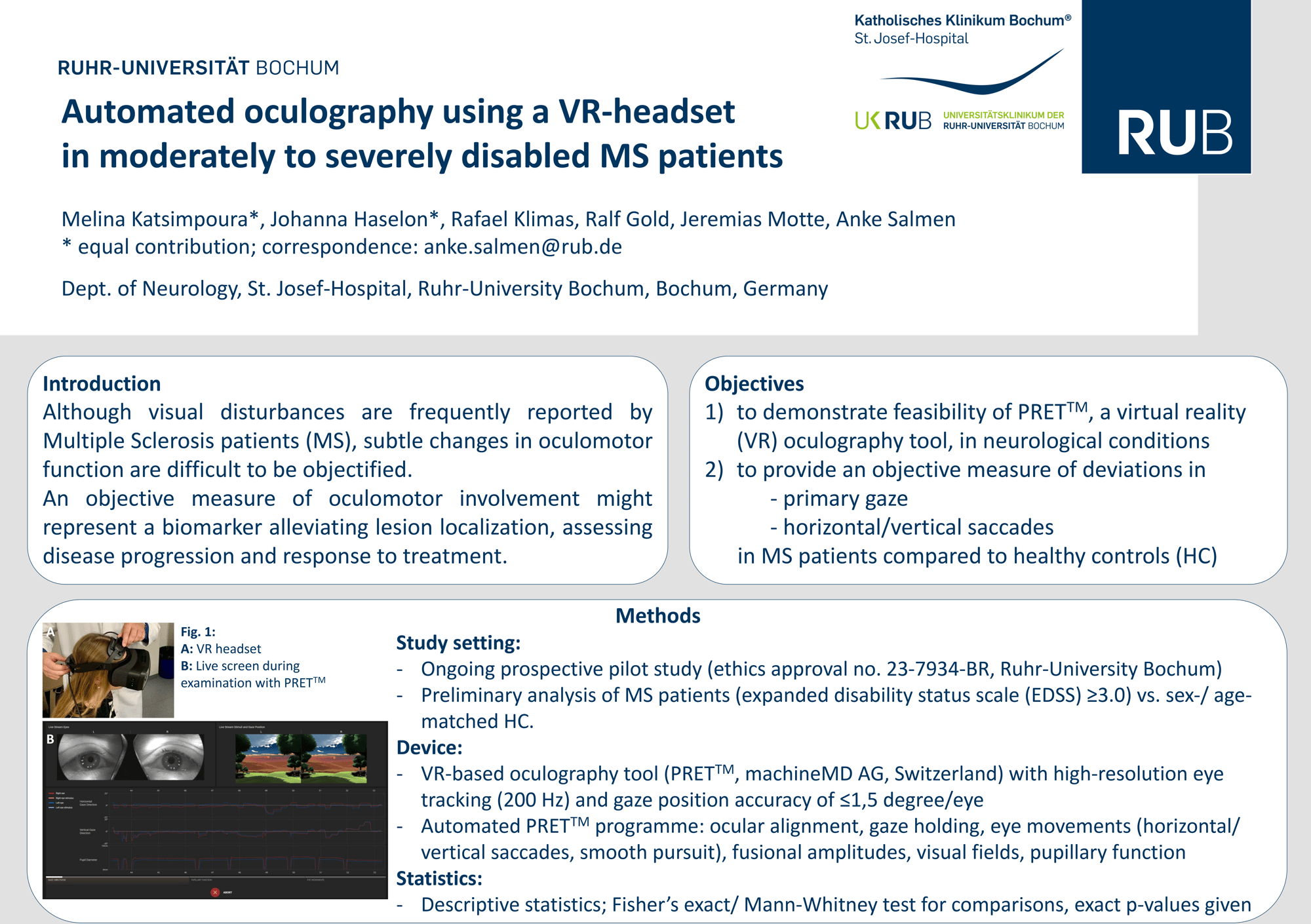
Automated oculography using a VR-headset in moderately to severely disabled MS patients
Presented by PD. Dr. med. Anke Salmen, Neurology Outpatient Clinic at the University Hospital of the Ruhr-University Bochum
Paper Poster Session 2 - Wednesday, 18 September 2024
Imaging and Non-imaging Biomarkers - Other Biomarkers

Optic neuritis is one of the most common forms of presentation in multiple sclerosis: in 25% of new MS cases optic neuritis is the initial clinical event. Moreover, studies show that 50-70% of all patients with MS will experience optic neuritis at some stage of the condition. Optic neuritis presents with acute unilateral vision loss1 - 3. Visual field defects are present in almost all patients with optic neuritis (97.5%)1. Relative afferent pupillary defects (RAPD) occur in 96% of acute unilateral optic neuritis cases4.
The most frequently observed eye movement disorders in MS are saccadic dysmetria (91%), INO (68%), vestibulo-ocular reflex abnormalities and gaze-evoked nystagmus (36%), fixation instability, and impaired smooth pursuit 1,5 . Up to 71% of INOs are not detected in routine clinical assessment6.
1 Frohman EM, Frohman TC, Zee DS, McColl R, Galetta S. The neuro-ophthalmology of multiple sclerosis. Lancet Neurol. 2005;4(2):111-121.
2 Dhanapalaratnam R, Markoulli M, Krishnan AV. Disorders of vision in multiple sclerosis. Clin Exp Optom. 2022;105(1):3-12.
3 Sheehy CK, Beaudry-Richard A, Bensinger E, Theis J, Green AJ. Methods to Assess Ocular Motor Dysfunction in Multiple Sclerosis. J Neuroophthalmol. 2018;38(4):488-493.
4 Cox TA, Thompson HS, Corbett JJ. Relative afferent pupillary defects in optic neuritis. Am J Ophthalmol. 1981;92(5):685-690.
5 Niestroy A, Rucker JC, Leigh RJ. Neuro-ophthalmologic aspects of multiple sclerosis: Using eye movements as a clinical and experimental tool. Clin Ophthalmol. 2007;1(3):267-272.
6 Frohman TC, Frohman EM, O'Suilleabhain P, et al. Accuracy of clinical detection of INO in MS: corroboration with quantitative infrared oculography. Neurology. 2003;61(6):848-850.

8 exams in under 12 minutes:
![]() gaze holding
gaze holding
![]() ocular alignment
ocular alignment
![]() fusional amplitudes
fusional amplitudes
![]() saccades
saccades
![]() smooth pursuit
smooth pursuit
![]() visual field screening
visual field screening
![]() afferent pupillary function
afferent pupillary function
![]() efferent pupillary function
efferent pupillary function
Let's keep in touch!
Please share your details with the machineMD team via the form below to learn more about clinical and research possibilities with neos™



